See your public IP, ISP name, and geolocation in real time.
Our tool also shows your local machine IP, making it easy to share accurate details with IT support teams for faster troubleshooting.
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique number assigned to each device connected to a computer network (like the internet). It works like a “digital home address,” allowing devices to find and communicate with each other.
Two categories of IP addresses
1. IPv4 (e.g., 192.168.1.1) – older, uses 32-bit numbers.
2. IPv6 (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334) – newer, uses 128-bit numbers, created because IPv4 addresses were running out.
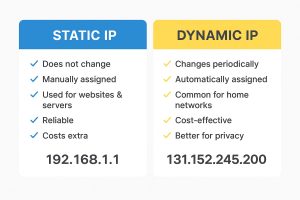
Static vs Dynamic IP Addresses
1. Static IP
A static IP address does not change.
It’s manually assigned and stays the same every time the device connects.
Commonly used for:
Websites & servers (so users can always reach them at the same address).
Remote access (e.g., CCTV systems, FTP servers).
Pros: Reliable, easy for hosting services.
Cons: Costs extra from ISPs, less private since it doesn’t change.
2. Dynamic IP
A dynamic IP address is automatically assigned by your ISP and can change every time you connect.
Most home networks use dynamic IPs.
Pros: Cheaper, better for privacy, no manual setup.
Cons: Not ideal for hosting servers or services that need a fixed address. Public & private IP Testing